Learn About High-Precision Lapping Film Abrasives for Polishing Different Materials?
Learn About High-Precision Lapping Film Abrasives for Polishing Different Materials
High-precision lapping film abrasives are essential tools in industries that require extremely fine surface finishes and high material removal control. These abrasives come in different types, each suited for polishing specific materials. From diamond and aluminum oxide to silicon carbide and cerium oxide, each abrasive plays a critical role in ensuring smooth, defect-free surfaces on a variety of materials, from optics to semiconductors.
This article will guide you through the different types of high-precision lapping film abrasives, their properties, applications, and how they help achieve superior finishes across various materials.
What Is Lapping Film?
Lapping film is a flexible abrasive sheet, usually made of polyester, with abrasive particles bonded to the surface. These abrasives come in a wide range of micron sizes and abrasive types to accommodate the specific polishing needs of materials such as metals, ceramics, glass, and plastics. The film's flexibility allows it to conform to the material's surface, ensuring uniform polishing and smooth results.
Lapping films are ideal for final polishing and defect removal, offering precise and consistent results in industries where surface quality is critical.
Types of High-Precision Lapping Film Abrasives
There are several types of abrasives used in high-precision lapping films, each designed to work effectively on specific materials. Below are the most commonly used types of lapping film abrasives:
1. Diamond Lapping Film
-
Best for: Hard materials such as ceramics, metals, optical components, semiconductors, and fiber optics.
-
Properties: Diamond abrasives are the hardest known material, providing high material removal rates with exceptional surface finishes. Diamond lapping films are known for their ability to polish very hard materials without damaging them.
-
Applications:
-
Fiber optic connector polishing (e.g., MTP/MPO, LC, SC connectors)
-
Semiconductor wafer polishing
-
Optical lens and mirror polishing
-
Hard metal finishing, such as tungsten carbide and sapphire polishing.
-
2. Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) Lapping Film
-
Best for: General-purpose polishing of metals, ceramics, plastics, and composites.
-
Properties: Aluminum oxide is a relatively moderately abrasive material, which makes it versatile for a range of polishing applications. It offers controlled cutting action, making it ideal for intermediate polishing or finishing stages.
-
Applications:
-
Automotive polishing for metal parts
-
Surface preparation in medical device manufacturing.
-
Polishing optical components, glass, and plastics.
-
Semiconductors in early-stage polishing.
-
3. Silicon Carbide (SiC) Lapping Film
-
Best for: Brittle materials like glass, ceramics, and composite materials.
-
Properties: Silicon carbide is known for its hardness and sharp cutting ability, which makes it highly effective for rough polishing and shaping of hard, brittle materials. Silicon carbide lapping films provide efficient material removal and are particularly useful when a fast cut is needed.
-
Applications:
-
MPO MT Patch Cord Polishing
-
Glass polishing (such as glass lenses and displays)
-
Ceramic material finishing
-
Composite material processing (e.g., for the aerospace industry)
-
4. Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) Lapping Film
-
Best for: Soft materials like plastics, resins, and some metals.
-
Properties: Silicon dioxide abrasives are generally less aggressive compared to diamond or silicon carbide, which makes them suitable for final polishing or finishing softer materials without over-polishing or causing damage.
-
Applications:
-
Polishing softer metals such as aluminum
-
Fine finishing of plastic parts and optical displays
-
Surface smoothing of resins and coatings
-
5. Cerium Oxide (CeO₂) Lapping Film
-
Best for: Optical glass, lenses, and mirrors.
-
Properties: Cerium oxide is chemically active, making it an ideal choice for polishing optical materials to achieve a high-gloss finish. It provides exceptional control in fine polishing and defect removal for optical surfaces, offering high-quality results without leaving scratches.
-
Applications:
-
Polishing optical lenses and mirrors to optical clarity
-
LCD panel polishing
-
Final finishing of glass surfaces for optical equipment and displays
-
Micron Sizes of Lapping Films
Lapping films come in a variety of micron sizes, allowing for precise control over the polishing process. The finer the micron size, the smoother the finish you will achieve. Here’s a breakdown of the typical micron sizes used for different polishing stages:
| Micron Size | Grit Equivalent | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 30–60 µm | P400–P240 | Rough polishing, removing large defects |
| 15–30 µm | P800–P600 | Intermediate polishing, refining rough surfaces |
| 5–15 µm | P1200–P2000 | Fine polishing, smoothing scratches and defects |
| 1–5 µm | P4000–P8000 | High-precision polishing, creating ultra-smooth surfaces |
| 0.1–1 µm | P12000+ | Final polishing, achieving a mirror-like finish |
How Lapping Film Works
The lapping film works through the process of abrasive contact between the film and the material’s surface. During lapping, the abrasive particles on the film gradually wear down the surface of the material to achieve a desired smoothness and flatness. The flexibility of the film allows it to conform to the contours of the surface, ensuring an even polish.
Lapping films are typically used in the following steps:
-
Coarse Polishing: Start with a coarser abrasive film (larger micron size) to remove material and shape the surface.
-
Intermediate Polishing: Use a mid-range abrasive film to refine the surface and remove imperfections left by the coarse polish.
-
Fine Polishing: Transition to finer films for smoothing and preparing the surface for final polishing.
-
Final Polishing: Use the finest abrasive films (e.g., diamond or cerium oxide) to create a mirror-like finish or achieve optical clarity.
Applications of High-Precision Lapping Film Abrasives
High-precision lapping films are used across industries where smoothness and accuracy are paramount. Below are some of the most common applications:
1. Fiber Optics
-
Materials: Ceramic ferrules, fiber optic connectors
-
Application: Diamond / Aluminium Oxide / Silicon Carbide / Silicon Dioxide / Cerium Oxide lapping films are used to polish fiber optic connectors to reduce insertion loss and maintain low attenuation at the connection point, ensuring optimal signal transmission.
2. Semiconductors
-
Materials: Silicon wafers, gallium arsenide, other semiconductor materials
-
Application:
1.Diamond-based lapping films are used for wafer polishing to remove defects, improve flatness, and prepare the wafers for chip fabrication.
2.Aluminum oxide is also used in early-stage polishing to remove larger surface defects.
3. Optics and Displays
-
Materials: Glass, optical lenses, mirrors, LCD panels
-
Application: Cerium oxide lapping films are ideal for optical finishing, ensuring a scratch-free and high-gloss finish on optical glass and lenses for applications such as camera lenses, eyeglasses, and displays.
4. Aerospace and Automotive
-
Materials: Engine parts, turbine blades, precision machined components
-
Application: Aluminum oxide and silicon carbide lapping films are used to finish metal parts for aerospace and automotive applications, ensuring precision machining and surface integrity.
5. Medical Devices
-
Materials: Surgical tools, implants, medical device components
-
Application: Lapping films ensure that medical devices and surgical tools have smooth, biocompatible surfaces that reduce friction and wear, and provide comfort for patients.
Key Benefits of Lapping Film Abrasives
-
Uniform Surface Finish: Lapping films provide a consistent abrasive action, ensuring uniformity and smoothness across the surface.
-
High Precision: With micron-sized abrasives, lapping films enable precise control over material removal, ensuring high-quality finishes without damaging the material.
-
Versatility: Lapping films can be customized for a wide range of materials, from metals and ceramics to plastics and optical glass.
-
Efficiency: Lapping films allow for fast, efficient polishing, especially when compared to traditional polishing methods like hand polishing.
What other materials benefit from these abrasives?
High-precision abrasives are versatile and can be used to polish a wide range of materials, each benefiting from the specific characteristics of the abrasive types (diamond, aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, cerium oxide). Here's a breakdown of materials across various industries that benefit from these abrasives:
1. Metals
-
Materials: Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, brass, copper, and alloys
-
Benefit: High-precision abrasives, like diamond or aluminum oxide, are used for polishing metal surfaces to reduce roughness, improve wear resistance, and provide a high-quality finish. These abrasives are essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
2. Ceramics
-
Materials: Advanced ceramics (e.g., zirconia, alumina), porcelain, and other technical ceramics
-
Benefit: Ceramics, being hard and brittle, require abrasives like diamond or silicon carbide to achieve precise polishing without cracking or chipping. These abrasives help achieve smooth, uniform surfaces for components used in industrial applications, medical implants, and electronics.
3. Glass
-
Materials: Optical glass, window glass, lenses, and displays (e.g., LCD, OLED)
-
Benefit: Cerium oxide and diamond abrasives are ideal for glass polishing, providing scratch-free finishes and removing haze. These abrasives are crucial in the production of high-quality optical lenses, glass windows, and touchscreens for smartphones and other devices.
4. Plastics
-
Materials: Acrylic, polycarbonate, nylon, PVC, and other thermoplastics
-
Benefit: Silicon carbide and aluminum oxide abrasives help polish plastics to a smooth finish, often used in the production of clear plastic components for automotive, electronics, and medical devices. These abrasives can remove scratches and improve the optical clarity of plastic parts.
5. Composites
-
Materials: Carbon fiber, fiberglass, resin-based composites, and other advanced composite materials
-
Benefit: Silicon carbide and diamond abrasives are highly effective for polishing composite materials, which can be more challenging to polish due to their layered structure. These abrasives ensure the removal of surface defects, giving composite materials a smooth finish for aerospace, automotive, and marine applications.
6. Stone & Concrete
-
Materials: Marble, granite, limestone, and other natural and engineered stones
-
Benefit: Diamond abrasives are used extensively in stone and concrete polishing to achieve smooth surfaces and high-gloss finishes. The abrasives can also be used for surface preparation prior to sealing or coating in construction and architectural applications.
7. Semiconductors
-
Materials: Silicon wafers, gallium arsenide, and other semiconductor materials
-
Benefit: Diamond abrasives are used in the semiconductor industry for wafer polishing and planarization to ensure flat, defect-free surfaces crucial for semiconductor performance. Aluminum oxide is also used in early-stage polishing to remove larger surface defects.
8. Sapphire
-
Materials: Sapphire wafers, crystals, and lenses
-
Benefit: Diamond abrasives are essential for polishing sapphire due to its hardness. Used in optics, sapphire lenses, and in the LED industry, diamond abrasives achieve smooth, scratch-free finishes that enhance the material's optical properties.
9. Titanium and Titanium Alloys
-
Materials: Titanium, titanium alloys (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V)
-
Benefit: Aluminum oxide and silicon carbide abrasives are used to polish titanium and its alloys, providing a high-quality surface finish without damaging the material. These are essential in industries such as aerospace, medical implants, and marine applications.
10. Rubber
-
Materials: Natural rubber, synthetic rubber, elastomers
-
Benefit: Aluminum oxide and silicon carbide abrasives can be used for fine-tuning the finish of rubber components, which are often used in automotive parts, gaskets, seals, and conveyor belts. These abrasives help remove surface imperfections, improve texture, and enhance performance.
Conclusion
High-precision lapping film abrasives are indispensable tools for achieving superior surface finishes across industries where precision and quality are critical. Whether you’re polishing fiber optic connectors, semiconductor wafers, optical lenses, or aerospace components, the right lapping film can make a significant difference in the quality and performance of the finished product.
Explore our range of high-precision lapping films at polishingfilm.com to find the perfect abrasive solution for your needs. For personalized recommendations, contact us at sales@xytbrands.com.
-

Telecommunications
-

Automotive
-

Roller finishing
-
Electronics
-
Semiconductors
-

Aerospace
-

Optical Glass Crystal
-

Jewellery lapidary
-

Medical
-

Oil & Gas
-

Food Processing
-

Furniture and Wood industry
-

Metals Finish
-
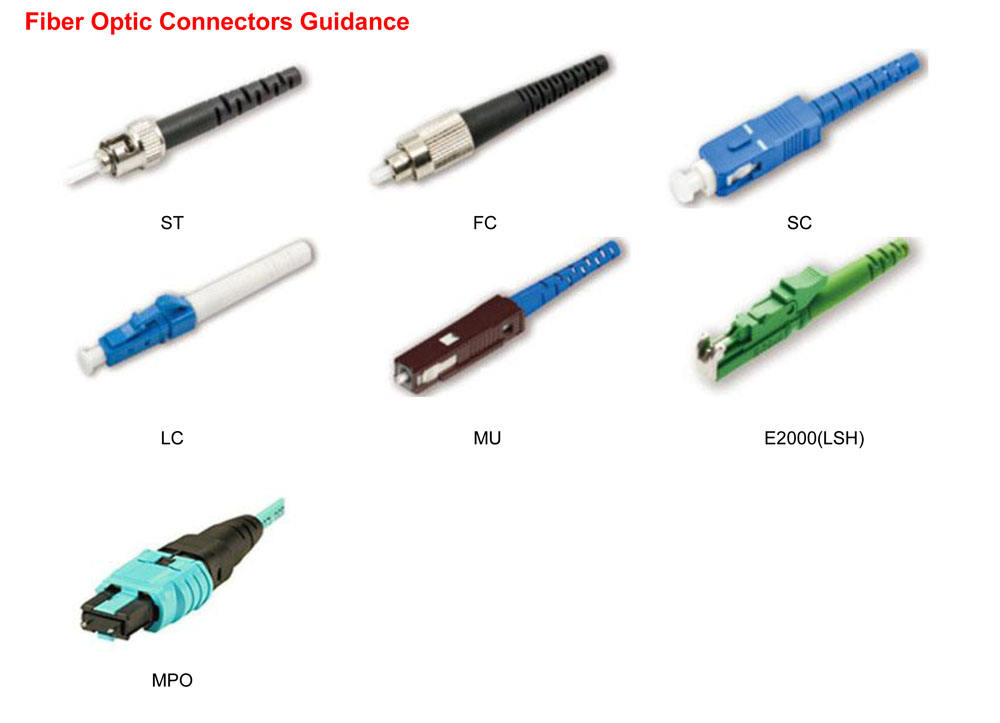

Fiber Optics Polishing
-

Music industry
-

LED LCD Panel
-

Mobile Phone Industry
-

Watch
-

Printing and Paper industry
-

Engine and Machine parts
-

Hydraulic components
-
Pneumatic components
-

Ball bearings
-

Gear and Train components
-

Moulds
-

Cranks Cams and Steering devices
-
Dental Polishing
-

Knife Blade Tools sharpening
-

Hard disks and Magnetic head
-
Other parts end face polishing




















































